Deutsch: Besatzungsquartiere / Español: Habitaciones de la tripulación / Português: Acomodações da tripulação / Français: Quartiers de l'équipage / Italiano: Quartieri dell'equipaggio
Crew quarters are designated living spaces for astronauts in spacecraft, space stations, or other space habitats, designed to provide a safe and comfortable Environment during missions.
Description
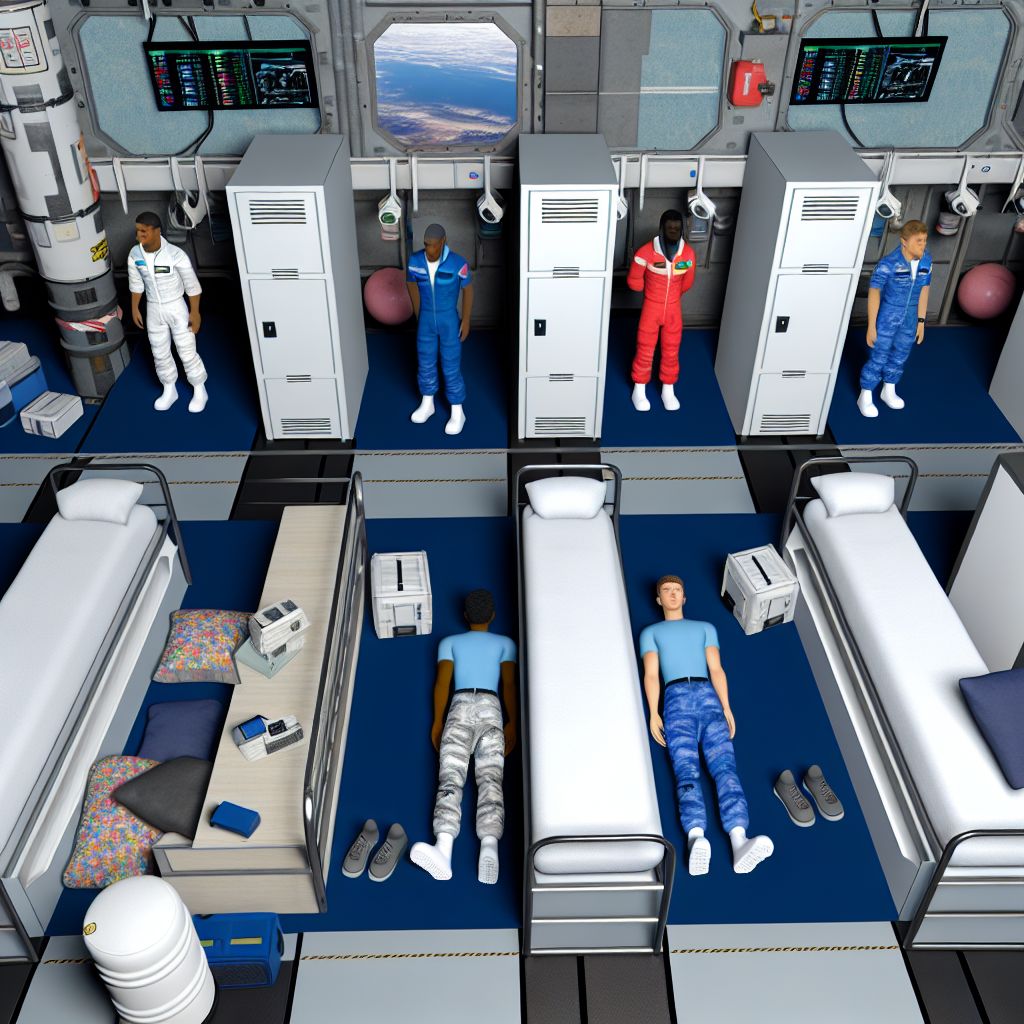
Crew quarters in the Space industry refer to the living areas provided for astronauts during space missions. These spaces are designed to ensure that crew members have a safe, functional, and somewhat comfortable environment where they can rest, sleep, and carry out personal activities. The Design of crew quarters considers factors such as limited space, microgravity, and the need for privacy and psychological well-being.
The quarters typically include sleeping areas, storage for personal items, and facilities for hygiene and relaxation. Given the unique challenges of space, these quarters are carefully engineered to optimize space, provide adequate Ventilation, and ensure the safety and health of the crew.
Application Areas
Crew quarters are essential in various types of space missions, including:
- International Space Station (ISS): The ISS has dedicated crew quarters with individual sleeping areas, personal storage, and facilities for personal hygiene and relaxation.
- Spacecraft for Long-Duration Missions: Spacecraft designed for missions to the Moon, Mars, or beyond include crew quarters that Support extended stays in space, focusing on the crew's comfort and psychological health.
- Commercial Space Stations: Emerging commercial space habitats also feature crew quarters designed to accommodate astronauts and space tourists for varying mission durations.
Well-Known Examples
- International Space Station (ISS): Each astronaut has a personal crew quarter, a small booth equipped with a sleeping bag, ventilation, lighting, and space for personal items.
- Orion Spacecraft: NASA’s Orion spacecraft, designed for deep space missions, includes crew quarters that provide sleeping and personal areas for astronauts on long-duration missions.
- SpaceX Dragon: The Dragon spacecraft includes sleeping arrangements and personal space for astronauts during their journey to and from the ISS.
Treatment and Risks
Designing crew quarters for space missions involves addressing several risks and challenges:
- Microgravity Adaptation: Ensuring that sleeping arrangements and personal spaces are functional in a microgravity environment, preventing issues like muscle atrophy and bone Density loss.
- Privacy and Psychological Health: Providing adequate privacy and personal space to support the psychological well-being of astronauts, who may spend extended periods in close quarters with others.
- Space Utilization: Maximizing the use of limited space while ensuring that the quarters are comfortable and meet all safety requirements.
To mitigate these risks, crew quarters are designed with careful consideration of human factors Engineering, incorporating feedback from astronauts and leveraging advances in materials and space habitat design.
Similar Terms
- Habitat Modules: Larger living spaces in space stations or habitats designed for extended missions, encompassing crew quarters and additional facilities for living and working.
- Sleeping Pods: Small, enclosed areas specifically designed for sleeping in space, often incorporated within crew quarters.
- Personal Storage Units: compartments within crew quarters where astronauts can store personal items securely and efficiently.
Summary
Crew quarters are a vital Component of spacecraft and space habitats, providing astronauts with essential living spaces that ensure their safety, comfort, and well-being during missions. These quarters are designed to address the unique challenges of space travel, including microgravity, limited space, and the need for privacy and psychological health, thereby contributing significantly to the success of space missions.
--
Related Articles to the term 'Crew Quarters' | |
| 'Spacecraft Interior' | ■■■■■■■■■■ |
| Spacecraft Interior: Spacecraft interior refers to the design, layout, and functionality of the inside . . . Read More | |
| 'Habitat' | ■■■■■■■ |
| Habitat: In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors . . . Read More | |
| 'Evacuation' | ■■■■■■ |
| Evacuation in the space industry context refers to the process of safely removing astronauts or personnel . . . Read More | |
| 'Zero Gravity' | ■■■■■ |
| Zero Gravity (\"zero-G\" or \"microgravity\") refers to the condition of near Weightlessness that occurs . . . Read More | |
| 'Fuselage' | ■■■■■ |
| Fuselage: In the Aerospace industry, the fuselage is the main body of an aircraft. It is the structure . . . Read More | |
| 'ISS' | ■■■■■ |
| ISS stands for International Space Station. The International Space Station is a space station, or a . . . Read More | |
| 'Environmental Stability' | ■■■■■ |
| Environmental Stability in the space industry refers to the ability to maintain a controlled and sustainable . . . Read More | |
| 'Water Recovery System' | ■■■■■ |
| Water Recovery System: Water recovery system in the space industry refers to a Technology or set of processes . . . Read More | |
| 'Noise cancellation' | ■■■■■ |
| Noise cancellation in the space industry refers to the techniques and technologies used to reduce or . . . Read More | |
| 'Aging' | ■■■■■ |
| Aging in the context of the space industry refers to the gradual Degradation and wear of spacecraft materials, . . . Read More | |
