Deutsch: Hauptteile einer Rakete in Originalgröße / Español: Partes principales de un cohete a escala real / Português: Principais partes de um foguete em tamanho real / Français: Principales parties d'une fusée à pleine échelle / Italiano: Principali parti di un razzo a dimensioni reali /
There are four major systems of a full-Scale Rocket:
- Structure System
- Payload System
- Guidance System
- Propulsion System
in future articles, you will find more details on these topics. Until then, you could drop your queries in a Forum section.
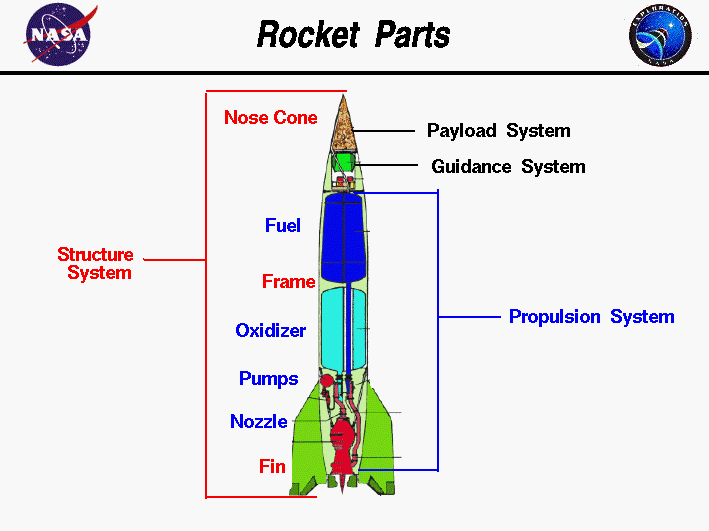
The major parts of a full-scale rocket in the aerospace context can vary depending on the specific rocket design and application. However, here are some common components and subsystems that are typically found in most rockets:
-
Nosecone: The pointed tip of the rocket that helps reduce drag and improve the rocket's aerodynamics.
-
Payload: The cargo or equipment that the rocket is carrying. This could include satellites, scientific instruments, or crew members.
-
Propulsion system: The system that generates the thrust needed to lift the rocket off the ground and accelerate it to its desired velocity. This includes the rocket engines, fuel tanks, and associated plumbing.
-
Avionics: The electronic systems that control the rocket's flight and monitor its performance. This includes the guidance, navigation, and control systems, as well as the telemetry and communication systems.
-
Fairing: The protective Enclosure that surrounds the payload and protects it during launch and ascent.
-
Fins: The stabilizing surfaces on the rear of the rocket that help control its direction and stability during flight.
-
Interstage: The section of the rocket that connects the various stages or components of the rocket together.
-
Parachutes: The devices that slow down the rocket's descent and help it land safely after separation from its payload.
-
Heat shield: The protective material that shields the rocket from the extreme heat generated during re-entry into the Earth's atmosphere.
-
Stage separation system: The mechanism that separates the rocket's stages or components after they have completed their mission.
Additional components that may be present in certain rockets include reaction control systems for attitude control, solar panels for power generation, and propulsion systems for in-flight course corrections.
Overall, the major parts of a full-scale rocket are designed to work together to accomplish the rocket's mission, whether that is launching a satellite into orbit, exploring deep Space, or carrying humans to other planets.
Related Articles to the term 'Major parts of a full scale rocket' | |
| 'Rocketry' | ■■■■■■■ |
| Rocketry is the Science, Technology, and engineering of designing, building, and launching rockets and . . . Read More | |
| 'Component' | ■■■■■■ |
| Component: In the aerospace industry, a component refers to the parts that make up an Aircraft, spacecraft, . . . Read More | |
| 'Two-stage' | ■■■■■■ |
| Two-stage in the Space industry refers to a rocket design that uses two separate propulsion stages to . . . Read More | |
| 'Launch Vehicle Engineering' | ■■■■■■ |
| Launch Vehicle Engineering refers to the design, Development, and Optimization of rockets or vehicles . . . Read More | |
| 'Research' | ■■■■■■ |
| Research is the process for increasing the stock of knowledge by creative and systematic work. . . . Read More | |
| 'SEMS' | ■■■■■■ |
| SEMS stands for Spacecraft Electrical, Mechanical, and Software Systems. It refers to the various electrical, . . . Read More | |
| 'Fluid' | ■■■■■■ |
| Fluid: In Physics, a fluid is a Liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (flows) under . . . Read More | |
| 'Launch' | ■■■■■ |
| Launch: A launch is the first part of the flight of a rocket when it leaves the ground for orbital spaceflights, . . . Read More | |
| 'Cluster' | ■■■■■ |
| A cluster refers to a group or arrangement of objects or systems that are connected or related in some . . . Read More | |
| 'Booster' | ■■■■■ |
| A booster refers to a rocket or propulsion system designed to provide the initial thrust needed to lift . . . Read More | |
